
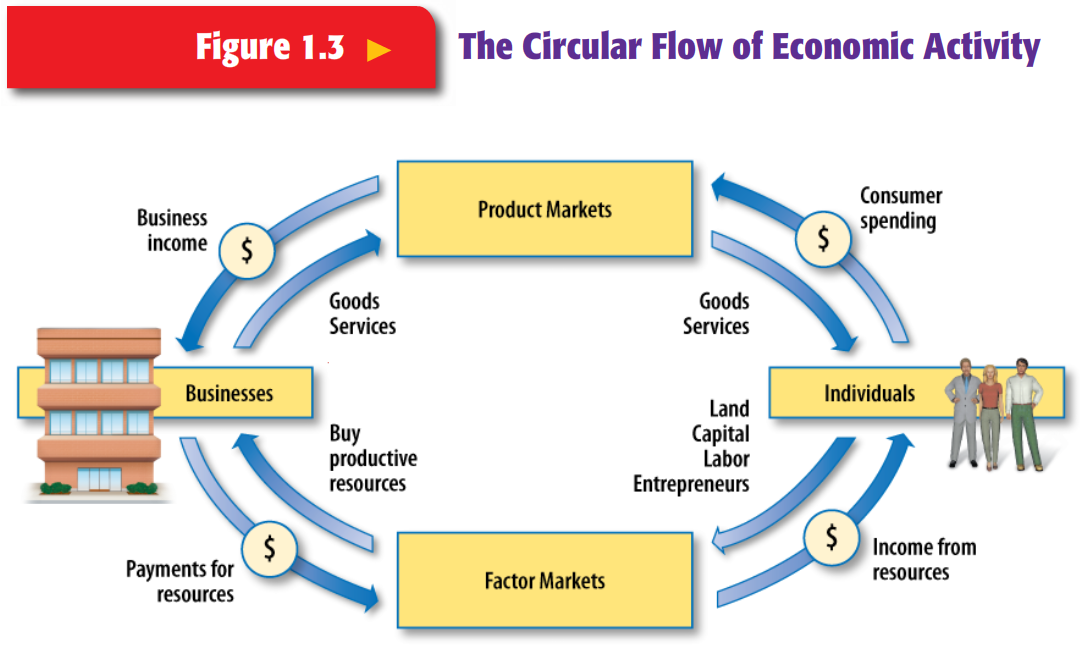
These factors are used by firms to produce goods and services, which are then sold to households in the goods market.

The factor market is a market where factors of production, such as labor, capital, and land, are bought and sold. The interaction between demand and supply in the product market determines the prices of goods and services and the quantity of goods and services that are exchanged.
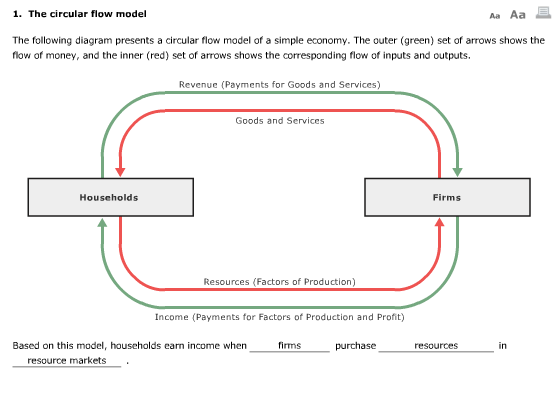
The supply of goods and services in the product market, on the other hand, is determined by firms' ability and willingness to produce and sell these goods and services at different prices. The demand for goods and services in the product market is driven by households' and businesses' income and their willingness and ability to purchase these goods and services. The product market plays a crucial role in the economy, as it is through the sale of goods and services that firms are able to generate revenue and profits. In the circular flow diagram, the product market represents the exchange of goods and services for money between firms and households. The product market is a market where firms sell the goods and services that they produce to households and businesses. Firms supply goods to the product market and receive payment for those goods. Firms receive factors of production, such as land, labor, and capital, from the factor market, and pay for them with wages or costs (wages for labor, costs for capital). Any business that produces a good is known as a firm. Firmsįirms are the producers in the economy. They receive wages, or income, from the factor market. Consumers also interact with the factor market, in which they provide a factor of production, labor. The product market gives consumers the goods that they demand.
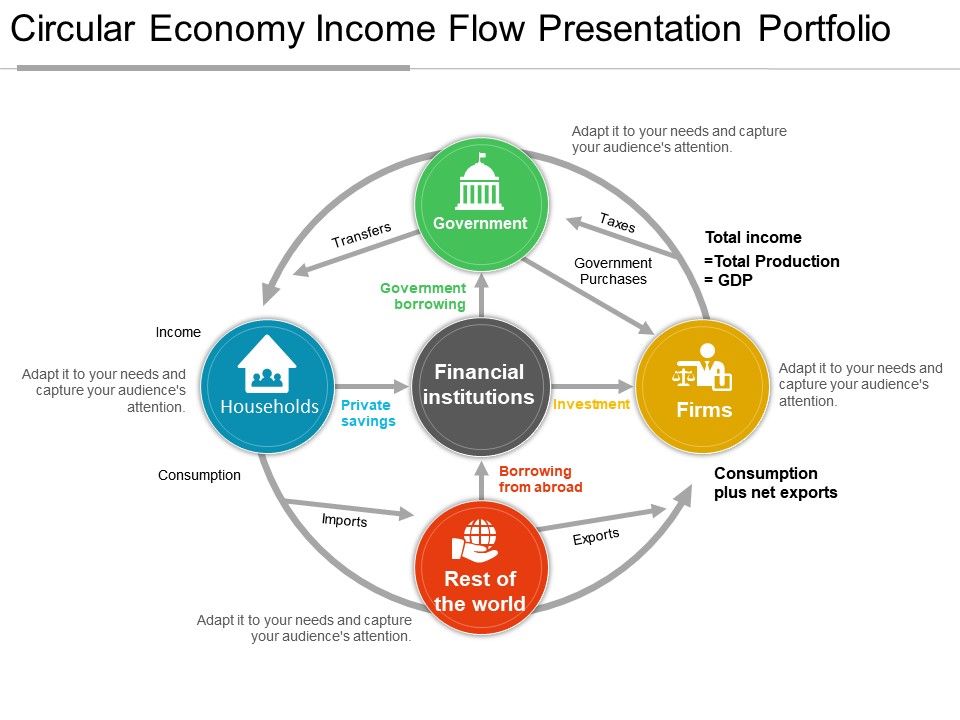
Consumers send money to the product market by buying goods. This means you, me, and everyone else around us are consumers. It can be estimated using one of three methods: looking at total expenditure, at total income or using the production approach.Let's break down each piece of the circular flow diagram.Ĭonsumers are the people buying goods in the economy. The way of measuring all these flows of money is the gross domestic product (GDP). However, this diagram introduces a clear view of how the economy works. Things such as government spending (in the form of unemployment benefits, for example) or government income ( taxes) are not shown in the diagram. For instance, take government intervention. There are a few things that are not showed in this diagram that must be taken into account to really understand how the economy of a country works. It’s worth mentioning that, as usually, diagrams do not shown how the economy actually works. The exchanges made in the economy imply a redistribution of rent according to the diagram, and the creation of value makes the economy grow. When we combine both diagrams, we get the circular-flow diagram, as shown below. Factors of production flow form households (red arrow) to firms, so they can produce more goods and services. In this case, money flows from firms to households (green arrow in the diagram below) in the form of wages in exchange for labour, interests for capital and rent for the use of land. Firms use these factors in their production. The market for factors of production is the place where households offer their labour, capital and other factors such as land, receiving an income for their use. In this case, the flow of money (green arrow in the diagram below) goes from households to firms, in exchange for finished products, which flow from firms to households (red arrow). This market represents the place where money and goods are exchanged. In other words, is the place where firms sell the goods and services they have produced, receiving a revenue paid by households. The market for goods and services is the place where households spend their money buying goods and services produced by firms. market for factors of production (such as labour or capital), where firms purchase factors of production from households in exchange for money. market for goods and services, where households purchase goods and services from firms in exchange for money The circular-flow diagram (or circular-flow model) is a graphical representation of the flows of goods and money between two distinct parts of the economy:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
